langchain4j-spring 学习
介绍
langchain4j-spring 是 LangChain4j 下支持 Spring Starter
机制的仓库
截止到当前版本 0.31.0 来看,仓库下的 module
主要分为两大类
流行的集成的 Starter(popular integrations)
langchain4j-open-ai-spring-boot-starter:OpenAI LLM
langchain4j-azure-open-ai-spring-boot-starter:Azure OpenAI LLM
langchain4j-anthropic-spring-boot-starter:Anthropic
LLM(Claude)
langchain4j-ollama-spring-boot-starter:Ollama LLM
AiService、RAG、Tools 等工具的 Starter
langchain4j-spring-boot-starter:核心能力
langchain4j-easy-rag-spring-boot-starter
需要注意的是,LangChain4j 支持 Java 8,但是这个 Spring Starter
项目只支持 Java 17(本质原因还是新的 Spring Boot 版本对 Java
版本的要求,如今新的 Spring 相关仓库很少支持 Java 8 了)
下面会简单了解一些核心功能的用法,以及实现方式
LLM
这里以 Azure OpenAI 为例
使用
在 application 文件中进行相关配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 langchain4j: azure-open-ai: chat-model: api-key: 'AZURE_OPENAI_KEY' endpoint: 'AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT' deployment-name: 'deploymentName' max-tokens: 1000
依赖自动注入,LLM 已经作为 Bean 实例化进容器了
接口为 dev.langchain4j.model.chat.ChatLanguageModel
实现类为
dev.langchain4j.model.azure.AzureOpenAiChatModel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Service @Slf4j public class MyLlmService { @Autowired private ChatLanguageModel chatLanguageModel; @PostConstruct public void post () { UserMessage message = UserMessage.from("Hello World" ); Response<AiMessage> generate = chatLanguageModel.generate(message); log.info("response content:{}" , generate.content()); } }
源码
自动装配
META 文件中指明了自动装配类为
dev.langchain4j.azure.openai.spring.AutoConfig
AutoConfig 主要负责如下相关 Bean 的装配工作
AzureOpenAiChatModel
AzureOpenAiStreamingChatModel
AzureOpenAiEmbeddingModel
AzureOpenAiImageModel
AzureOpenAiTokenizer
以 AzureOpenAiChatModel 和
AzureOpenAiTokenizer 为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @AutoConfiguration @EnableConfigurationProperties(Properties.class) public class AutoConfig { @Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(Properties.PREFIX + ".chat-model.api-key") AzureOpenAiChatModel openAiChatModelByAPIKey (Properties properties) { return openAiChatModel(properties); } ... @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean AzureOpenAiTokenizer openAiTokenizer () { return new AzureOpenAiTokenizer (); } }
可以看到当发现存在配置 .chat-model.api-key
时,将会实例化 AzureOpenAiChatModel
后面的 openAiChatModel
方法会根据配置文件内容创建出相关实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 AzureOpenAiImageModel openAiImageModel (Properties properties) { ImageModelProperties imageModelProperties = properties.getImageModel(); AzureOpenAiImageModel.Builder builder = AzureOpenAiImageModel.builder() .endpoint(imageModelProperties.getEndpoint()) .apiKey(imageModelProperties.getApiKey()) .deploymentName(imageModelProperties.getDeploymentName()) .size(imageModelProperties.getSize()) .quality(imageModelProperties.getQuality()) .style(imageModelProperties.getStyle()) .user(imageModelProperties.getUser()) .responseFormat(imageModelProperties.getResponseFormat()) .timeout(imageModelProperties.getTimeout() == null ? null : Duration.ofSeconds(imageModelProperties.getTimeout())) .maxRetries(imageModelProperties.getMaxRetries()) .proxyOptions(ProxyOptions.fromConfiguration(Configuration.getGlobalConfiguration())) .logRequestsAndResponses(imageModelProperties.getLogRequestsAndResponses() != null && imageModelProperties.getLogRequestsAndResponses()); if (imageModelProperties.getNonAzureApiKey() != null ) { builder.nonAzureApiKey(imageModelProperties.getNonAzureApiKey()); } return builder.build(); }
这里的就是在获取配置文件中的属性进行实例化
这里多说一句!
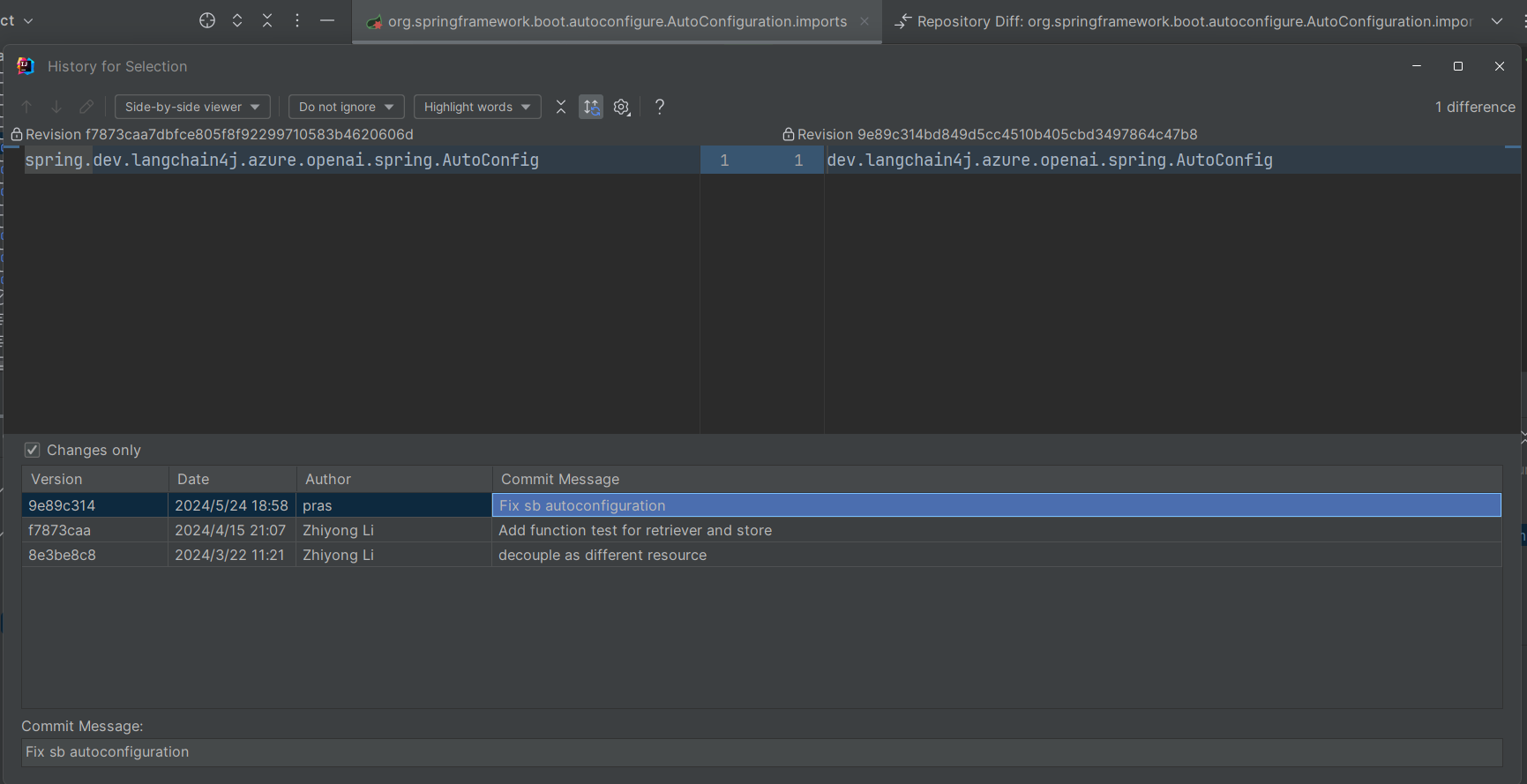
一开始我的项目启动不起来,报错信息如下,明显是装配类的全限定名路径错了,前面多了一个
spring.
1 Unable to read meta-data for class spring .dev.langchain4j.azure.openai.spring.AutoConfig
我看了一下代码,发现项目中写的确实是
dev.langchain4j.azure.openai.spring.AutoConfig spring
,所以我的怀疑重心就放在了 Spring 和 Maven
的编译插件上了,以为是换了新版本的 Spring Boot 有什么新机制导致的
“水土不服”
结果怎么试都不行,实在没办法了看了一下提交时间,发现竟然是 5.24
才进行的 fix,也就是说在仓库的 0.32.0-SNAPSHOT
是修复过的,而之前的 0.31.0 这个 RELEASE
版本,就是错的…
没办法,本地打了一个 0.32.0-SNAPSHOT 包继续测试
那么为什么会出现这种错误呢,因为这个贡献者还写了了 Azure Search 的
Starter,在那个 module 下,AutoConfig 是在
dev.langchain4j.azure.openai.spring
这个路径,所以我猜测是作者搞混了
配置
这里简单看下都有哪些配置参数
具体的属性都在
dev.langchain4j.azure.openai.spring.Properties
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Getter @Setter @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = Properties.PREFIX) public class Properties { static final String PREFIX = "langchain4j.azure-open-ai" ; @NestedConfigurationProperty ChatModelProperties chatModel; @NestedConfigurationProperty ChatModelProperties streamingChatModel; @NestedConfigurationProperty EmbeddingModelProperties embeddingModel; @NestedConfigurationProperty ImageModelProperties imageModel; }
以聊天模型为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Getter @Setter class ChatModelProperties { String endpoint; String apiKey; String nonAzureApiKey; String organizationId; String deploymentName; Double temperature; Double topP; Integer maxTokens; Double presencePenalty; Double frequencyPenalty; String responseFormat; Integer seed; List<String> stop; Integer timeout; Integer maxRetries; Boolean logRequestsAndResponses; }
这里就是支持的所有参数了,可以看到使用示例中的属性皆在这里
apiKey
endpoint
deploymentName
maxTokens
AiService
使用
定义接口,标注 @AiService
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @AiService public interface MyAiService { @SystemMessage(""" Tell me five names about the topic given by users. Separate with commas. """) String answer (String userMessage) ; }
注入后使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Component @Slf4j public class Run { @Autowired private MyAiService myAiService; @PostConstruct public void post () { String resp = myAiService.answer("国家首都" ); log.info("response content:{}" , resp); } }
源码
AiService Bean 的创建是通过
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现的
dev.langchain4j.service.spring.AiServicesAutoConfig
组件获取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class AiServicesAutoConfig { @Bean BeanFactoryPostProcessor aiServicesRegisteringBeanFactoryPostProcessor () { return beanFactory -> { String[] chatLanguageModels = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(ChatLanguageModel.class); String[] streamingChatLanguageModels = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(StreamingChatLanguageModel.class); String[] chatMemories = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(ChatMemory.class); String[] chatMemoryProviders = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(ChatMemoryProvider.class); String[] contentRetrievers = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(ContentRetriever.class); String[] retrievalAugmentors = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(RetrievalAugmentor.class); ... }
AiService 依赖的大部分组件,都是在 Bean
容器内进行获取,例如 LLM、记忆等重要组件
扫描 @AiService
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private static Set<Class<?>> findAiServices(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { String[] applicationBean = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForAnnotation(SpringBootApplication.class); BeanDefinition applicationBeanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(applicationBean[0 ]); String basePackage = applicationBeanDefinition.getResolvableType().resolve().getPackage().getName(); Reflections reflections = new Reflections (basePackage); return reflections.getTypesAnnotatedWith(AiService.class); }
这里为了拿到 Application 的 basePackage,然后通过
Reflections 扫描所有带有 @AiService
注解的类
创建 Bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 GenericBeanDefinition aiServiceBeanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition (); aiServiceBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(AiServiceFactory.class); aiServiceBeanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(aiServiceClass); MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = aiServiceBeanDefinition.getPropertyValues(); AiService aiServiceAnnotation = aiServiceClass.getAnnotation(AiService.class); addBeanReference( ChatLanguageModel.class, aiServiceAnnotation, aiServiceAnnotation.chatModel(), chatLanguageModels, "chatModel" , "chatLanguageModel" , propertyValues );
拿到 Class 后,通过 BeanDefinition 的方式设置 Bean
后续的 addBeanReference 方法将组件添加到
AiService 的定义中
这里还需要注意,通过包装 AiServiceFactory
的方式进行创建的实现,这样可以将 Spring 包中的方式接入 Core
包的核心方法,让创建流程更加统一
对于工具解析相关的方法,是 AiServices 提供的
Spring 的封装这里主要是提供到对 Bean 扫描 @Tool
这一步
随后在 AiServiceFactory 的 getObject
实现上解析工具的相关属性
1 2 3 if (!isNullOrEmpty(tools)) { builder = builder.tools(tools); }
RAG
提供了对 RAG 相关组件 Embedding Store 自动装配的能力
实现上比较简单
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 @EnableConfigurationProperties(RagProperties.class) public class RagAutoConfig { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean EmbeddingStore<TextSegment> embeddingStore () { return new InMemoryEmbeddingStore <>(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean({ EmbeddingModel.class, EmbeddingStore.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean ContentRetriever contentRetriever (EmbeddingModel embeddingModel, EmbeddingStore<TextSegment> embeddingStore, RagProperties ragProperties) { EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.EmbeddingStoreContentRetrieverBuilder builder = EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.builder() .embeddingStore(embeddingStore) .embeddingModel(embeddingModel); if (ragProperties != null ) { RetrievalProperties retrievalProperties = ragProperties.getRetrieval(); if (retrievalProperties != null ) { builder .maxResults(retrievalProperties.maxResults) .minScore(retrievalProperties.minScore); } } return builder.build(); } }
其中 ContentRetriever 依赖 EmbeddingStore
和 EmbeddingModel,而对于存储,也提供了一个默认的
InMemoryEmbeddingStore 实现
实现一个 Agent
这里具体就看 langchain4j-examples 的代码吧
langchain4j-examples/customer-support-agent-example
at main · langchain4j/langchain4j-examples (github.com)
Spring
项目中的一些操作(特别是 Bean 装配)用到了一些少见的 Spring
能力,在这里整理一下
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
Factory hook that allows for custom modification of an application
context's bean definitions, adapting the bean property values of the
context's underlying bean factory.
在标准初始化( standard initialization)后修改上下文的内部 Bean 工厂
所有 Bean Definition 都将被加载,但还没有任何 Bean 被实例化
将允许重写或添加属性,甚至可以将其添加到 eager-initializing beans 中
>
所以 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 本质上就是用于增强 Bean
Definition 即元数据,此时 Bean 还没有进行实例化
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是一个函数式接口
1 2 3 4 @FunctionalInterface public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor { void postProcessBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
参数中提供的 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
可以用来枚举所有的 Bean Definition,从而可以进行修改 Bean Definition
信息等操作
也可以通过 getBean 系列方法获取 Bean 或将其初始化
示例
以 CustomAutowireConfigurer 举例,它是
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类,作用是用户自定义类似
@Qualifier 功能的注解
定义一个 Bean 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Data @Builder @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student { private Integer age; private String name; }
定义注解
1 2 3 4 5 @Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAutowired { String name () ; }
装配类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Configuration public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Bean @MyAutowired(name = "zhangsan") public Student zhangsanStudent () { return Student.builder().name("zhangsan" ).age(18 ).build(); } @Bean @MyAutowired(name = "lisi") public Student lisiStudent () { return Student.builder().name("lisi" ).age(19 ).build(); } @Bean public BeanFactoryPostProcessor initMyBeanFactoryPostProcessor () { CustomAutowireConfigurer customAutowireConfigurer = new CustomAutowireConfigurer (); customAutowireConfigurer.setCustomQualifierTypes(Set.of(MyAutowired.class)); return customAutowireConfigurer; } }
验证
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class MyAspect implements ApplicationListener <ContextRefreshedEvent> { @Autowired @MyAutowired(name = "lisi") private Student student; @Override public void onApplicationEvent (ContextRefreshedEvent event) { System.out.println("MyAspect student:" + student); } }
BeanPostProcessor
Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean
instances — for example, checking for marker interfaces or wrapping
beans with proxies.
工厂相关的钩子,允许自定义修改新的 Bean 实例 例如检查标记的接口或者给
Bean 包装代理 >
因为和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
名字很像,所以明确区分两个钩子区别很重要,另外也看一下
InitializingBean
java
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor and BeanPostProcessor in lifecycle events -
Stack Overflow
hook
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor
InitializingBean
生命周期
初始化完成 initialization
实例化中 instantiation
实例化完成
核心能力
获取、修改、添加 BeanDefinition
检查、增强 Bean
Bean 实例化完成后要做的操作
调用时机
所有 BeanDefinition 初始化完成
每个 Bean 实例化过程中,调用构造器前后
每个 Bean 实例化完成后
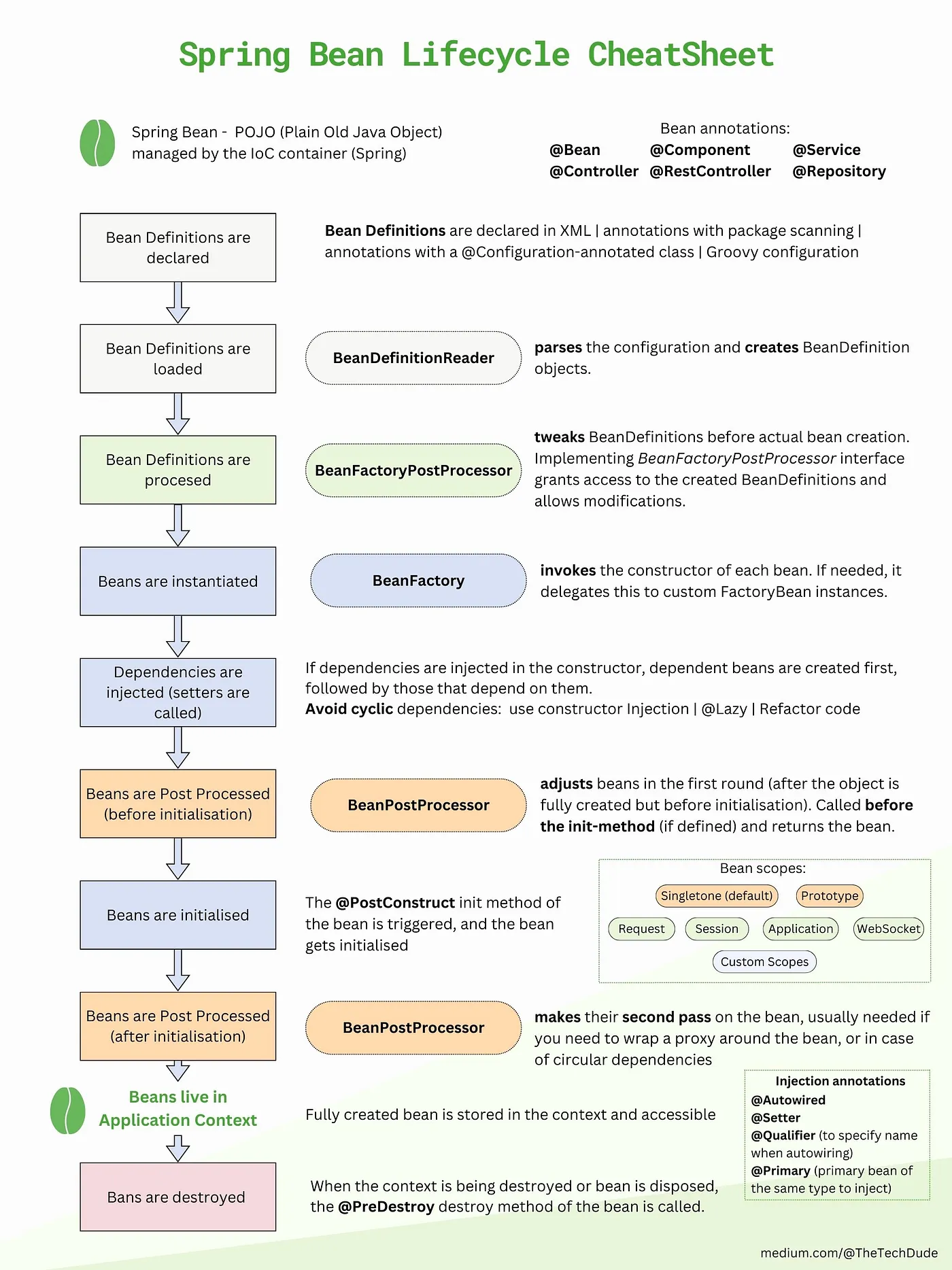
放一张老生常谈的生命周期图示
FactoryBean
If a bean implements this interface, it is used as a factory for an
object to expose, not directly as a bean instance that will be exposed
it self.
如果一个 Bean
实现了这个接口,那么它将会作为一个公开的工厂,而不是作为一个公开的 Bean
实例(也就是说这个工厂 Bean 是不公开的,其生产的实例是公开的) >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public interface FactoryBean <T> { @Nullable T getObject () throws Exception; @Nullable Class<?> getObjectType(); default boolean isSingleton () { return true ; } }
默认、需要实现的方法
getObject:返回构建的 BeangetObjectType:返回 Bean 的 Class
对象(我认为是为了解决泛型擦除)isSingleton:单例还是原型
示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Component public class StudentFactory implements FactoryBean <Student> { @Override public Student getObject () { return Student.builder() .name("this is a factory bean" ) .age(-1 ) .build(); } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return Student.class; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Component public class MyAspect implements ApplicationListener <ContextRefreshedEvent> { @Autowired private Student student; @Override public void onApplicationEvent (ContextRefreshedEvent event) { System.out.println("MyAspect student:" + student); } }
GenericBeanDefinition
GenericBeanDefinition 是
AbstractBeanDefinition 最基本的实现
需要通过 Bean Definition 来定义一个简单 Bean 时,就可以使用这个类,在
langchain4j-spring 中就使用它来补充 AiService 实现的
Bean
以下是一些 GenericBeanDefinition 的重要 API
setParentName :用于设置父 Bean 的名称,此 Bean
将继承父 Bean 的所有配置setBeanClassName :用于设置此 Bean 的全限定类名setScope :用于设置此 Bean 的作用范围,如
singleton 或 prototypesetPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues) :用于设置此
Bean 的属性值
参考
java
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor and BeanPostProcessor in lifecycle events -
Stack Overflow
Spring
Boot Integration | LangChain4j
langchain4j/langchain4j-spring:
LangChain4j integration with Spring (github.com)
langchain4j/langchain4j-examples
(github.com)